Health
Rise in Tick-Borne Illnesses: Dr. Scott Weese Addresses Concerns
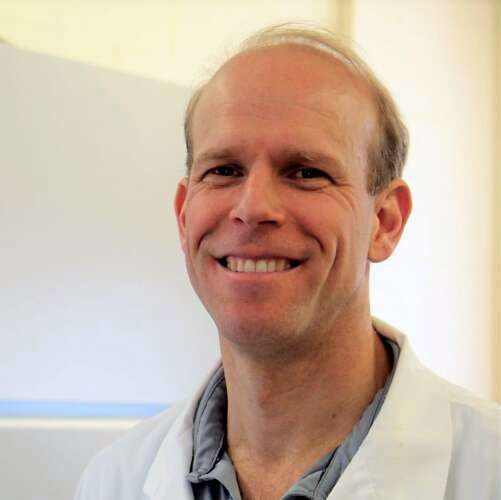

Dr. Scott Weese, the chief of infection control at the Ontario Veterinary College, recently highlighted concerns regarding a significant rise in cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever during an interview with CBC News. This tick-borne illness has seen an increase in reported cases, prompting health officials to take a closer look at the implications for public health.
Understanding Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii and is transmitted through the bite of infected ticks, particularly the American dog tick. Symptoms often include fever, headache, and a distinctive rash. If left untreated, the disease can lead to severe complications or even death. As of 2023, health authorities in Canada are observing a worrying trend in the frequency of this illness.
Dr. Weese explained that the increase in cases is likely influenced by a variety of factors, including climate change, which affects tick populations and their habitats. Warmer winters and milder summers are allowing ticks to thrive longer and spread into new areas. This change in ecosystem dynamics has raised alarms among health officials and researchers alike.
The Importance of Awareness and Prevention
In his discussion, Dr. Weese emphasized the need for increased public awareness regarding tick-borne illnesses. He urged individuals, particularly those who spend time outdoors, to take precautions such as wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent. Additionally, he recommended conducting tick checks after outdoor activities, especially in areas known for higher tick populations.
The rise in reported cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever serves as a critical reminder of the changing landscape of infectious diseases. As Dr. Weese noted, “We need to be proactive in understanding these trends and how they affect public health.” This perspective aligns with ongoing research aimed at developing better preventive measures and treatments for tick-borne diseases.
In summary, the growing incidence of Rocky Mountain spotted fever, as discussed by Dr. Scott Weese, highlights a pressing public health issue. With increasing tick populations and changing environmental conditions, the path forward requires heightened awareness and proactive measures to protect communities across Ontario and beyond.
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoScientists Unearth Ancient Antarctic Ice to Unlock Climate Secrets
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoTrump and McCormick to Announce $70 Billion Energy Investments
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoTransLink Launches Food Truck Program to Boost Revenue in Vancouver
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoFour Astronauts Return to Earth After International Space Station Mission
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoApple Notes Enhances Functionality with Markdown Support in macOS 26
-

 Top Stories1 week ago
Top Stories1 week agoUrgent Update: Fatal Crash on Highway 99 Claims Life of Pitt Meadows Man
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoSearch Underway for Missing Hunter Amid Hokkaido Bear Emergency
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoUkrainian Tennis Star Elina Svitolina Faces Death Threats Online
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoFrosthaven Launches Early Access on July 31, 2025
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoCarney Engages First Nations Leaders at Development Law Summit
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCalgary Theatre Troupe Revives Magic at Winnipeg Fringe Festival
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoShutdown Reflects Democratic Struggles Amid Economic Concerns