Science
Surprising Mechanisms of Flowers Enhance Pollination Efficiency
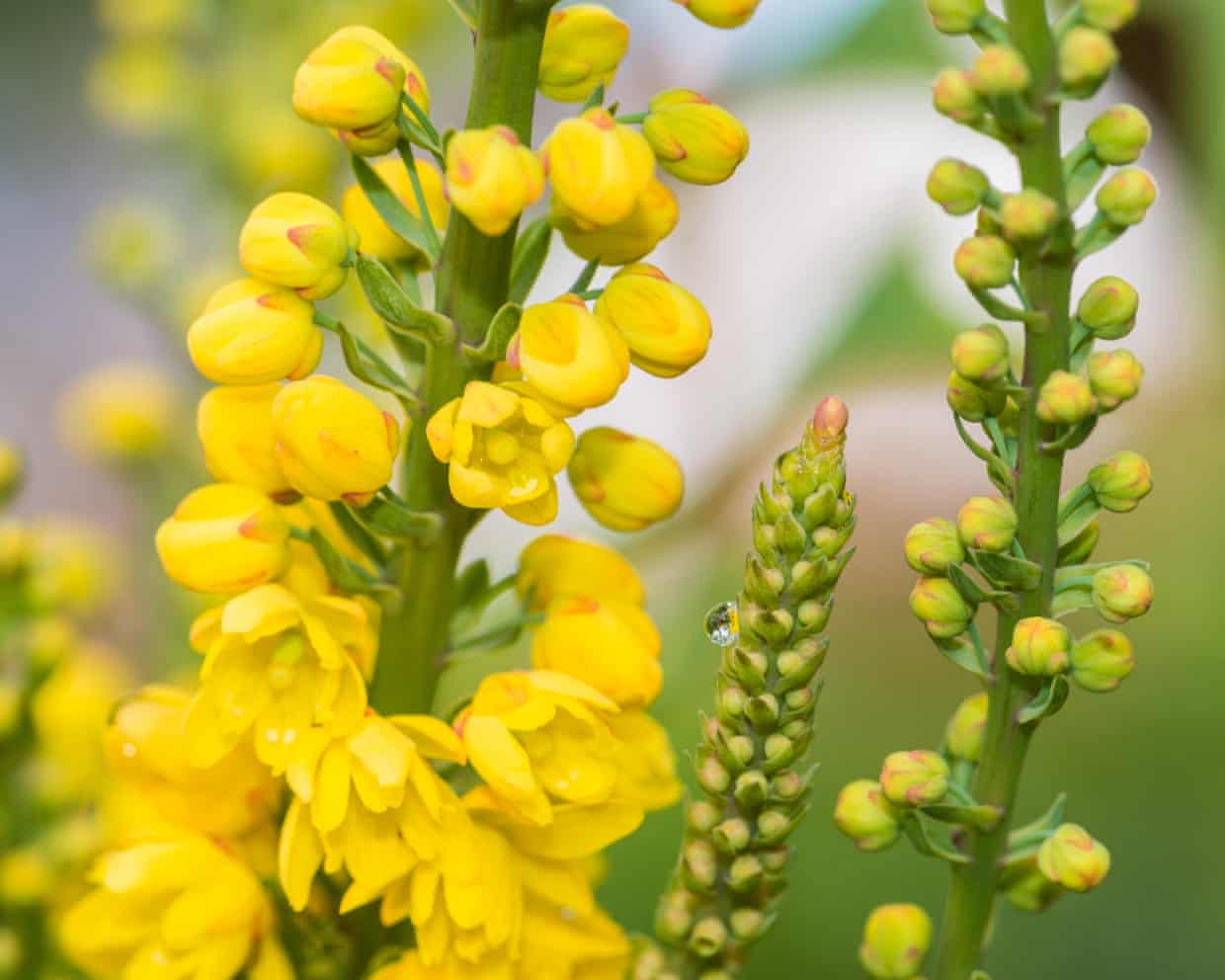

Research reveals that flowers, particularly their male reproductive parts known as stamens, exhibit remarkable behaviors to optimize pollination. Various plant species employ touch-sensitive stamen movements to interact with visiting pollinators, effectively managing their nectar and pollen resources.
Flowers belonging to the genera Berberis and Mahonia utilize a fascinating strategy where their stamens quickly bend over when an insect lands to feed on nectar. This action results in pollen being smothered onto the insect’s face or tongue. Such an unexpected encounter often causes the insect to limit its stay, thereby preventing the flower from depleting its nectar and pollen reserves. Subsequently, the insect transfers the pollen to another flower, facilitating cross-pollination when it brushes against the receptive female organs.
The orchid Catasetum takes a more aggressive approach. When an insect approaches, it experiences a swift and forceful action as sticky pollen bags eject at high speed, often dislodging the insect from the flower. The pollen bags adhere to the insect, ensuring that it carries the pollen to another plant.
Australian triggerplants, known as Stylidium, showcase yet another innovative method. These flowers feature a club-shaped organ that can swing through 180 degrees in an astonishing ten thousandths of a second. Upon contact, this organ strikes the visiting insect, covering it with pollen while simultaneously collecting any pollen it may possess. After this swift interaction, the trigger swiftly resets, ready for the next pollinator.
Such intricate mechanisms not only highlight the complexity of plant-pollinator interactions but also underscore the evolutionary adaptations that enhance reproductive success. Understanding these processes offers valuable insights into the broader ecological relationships within ecosystems. The strategic movements of stamens, whether they serve to control nectar access or to ensure effective pollen transfer, exemplify the critical role that flowers play in sustaining biodiversity.
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoSecwepemc First Nation Seeks Aboriginal Title Over Kamloops Area
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoScientists Unearth Ancient Antarctic Ice to Unlock Climate Secrets
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoTrump and McCormick to Announce $70 Billion Energy Investments
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoFour Astronauts Return to Earth After International Space Station Mission
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoTransLink Launches Food Truck Program to Boost Revenue in Vancouver
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoManitoba’s Burger Champion Shines Again Amid Dining Innovations
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoApple Notes Enhances Functionality with Markdown Support in macOS 26
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoUrgent Update: Fatal Crash on Highway 99 Claims Life of Pitt Meadows Man
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoHomemade Houseboat ‘Neverlanding’ Captivates Lake Huron Voyagers
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoUkrainian Tennis Star Elina Svitolina Faces Death Threats Online
-

 Sports5 months ago
Sports5 months agoSearch Underway for Missing Hunter Amid Hokkaido Bear Emergency
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoCarney Engages First Nations Leaders at Development Law Summit